electron sea model|rc seaview submarine for sale : Clark Using the “electron sea” model to explain it. Metallic bonding is an attraction between positively charged metal ions and a “sea” of surrounding negatively charged electrons. These valence electrons hold . Oh ngayon guys alam nyo na enjoy sa pagjakol. 1:03. Wala akong choice kundi e share sarap kasi. 11:11. Beautiful Filipino girlfriend in EXPOSED homemade sex video. 3:44. Kantot Sa Kotse ang Inabot ng Malibog Na Call Center Agent. 1:04. Ito ang trabaho mo, Isubo mo ang Titi ko. 1:10. Magastos man natitikman ko naman.
PH0 · seaview submarine filming miniature
PH1 · sea of electrons definition
PH2 · rc seaview submarine for sale
PH3 · model of metallic bonding
PH4 · metallic bonding diagram
PH5 · metal to metal bonding
PH6 · ionic covalent and metallic bonding
PH7 · electron sea model definition chemistry
PH8 · Iba pa
Authorised UK Kingston Reseller of genuine Kingston Memory, RAM, SSDs, Fury, Memory Cards & more. Free Delivery & Free returns on all products with a 100% moneyback guarantee.
electron sea model*******The electron-sea model is a model of metallic bonding in which cations are considered to be fixed points within a mobile 'sea' of electrons. Learn the definition, history, and applications of this model .
The metal is held together by the strong forces of attraction between the positive nuclei and the delocalized electrons (Figure 1 ). Figure 1: Metallic Bonding: The .Learn how metal atoms form metallic bonds with delocalized electrons, creating metals with high conductivity, malleability, and melting points. The electron sea model is a .electron sea model Using the “electron sea” model to explain it. Metallic bonding is an attraction between positively charged metal ions and a “sea” of surrounding negatively charged electrons. These valence electrons hold . This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into metallic bonding and the electron sea model. The valence electrons in the metal are delocal.
In the electron sea model, the valence electrons are free, delocalized, mobile, and not associated with any particular atom. This model may account for: Conductivity : Since the electrons are free, if electrons from .Learn about the electron sea model, a framework that explains the free nature of electrons around metal atoms and their properties. Find out how metallic bonding, . Properties of metals and how we can explain their properties using electron "sea" model.Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/.
Electron Sea Model. Most metal atoms do not possess enough valence electrons to enter into an ionic or covalent bonding. However, the valence electrons in metal atoms are loosely held due to their low . By the electron-sea model, we might think that more electrons makes the bonds stronger, so hardness and melt point would increase across the periodic table. .rc seaview submarine for sale The electron-sea model also enables us to explain, at least partially, why the metallic bond is noticeably stronger for some metals than others. While the alkali metals and some of the alkaline-earth metals can be cut with a knife, metals like tungsten are hard enough to scratch the knife itself. A good indication of how the strength of the .
Electron Sea Model Metals make up most of the elements in the periodic table (around 80%), and they are special. When metals bond with themselves, they bond in a different way than when they bond . The Electron Sea Model. The electron sea model is a simplistic and somewhat inaccurate view of metallic bonding, but it’s the easiest to visualize. In this model, a sea of electrons floats around a .
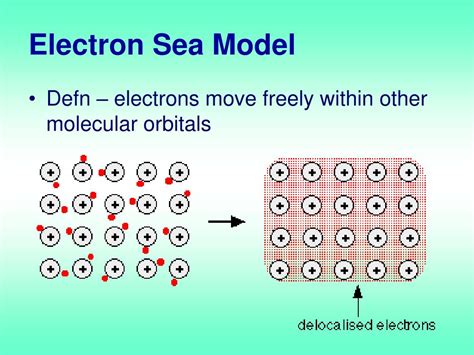
The Electron Sea Model** Consider sodium metal as an example. Sodium has the electronic structure 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1.When sodium atoms come together, the electron in the 3s atomic orbital of one sodium atom can share space with the corresponding electron on a neighboring atom to form a bond - in much the same sort of way that a covalent . tutorial on the electron sea model of metallic bonding and the model's relationship to metallic properties such as malleability, hardness, high melting point. Drude's electron sea model assumed that valence electrons were free to move in metals, quantum mechanical calculations told us why this happened. Metallic bonding in sodium. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Even a metal like sodium (melting point 97.8°C) melts .The electron sea model is used to explain several unique properties of metals. So far, we have looked at the electron sea model purely in terms of electrostatics: the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged nucleus. However, we already saw in the discussion of quantum mechanics in the atom that kinetic energy and the .Electron Sea Model . Figure 11.4.a. Pictorial representation of electron sea model. Atomic cores (nuclei and core electrons) form the "spheres" while valence electrons become attracted to multiple nuclei, and are free to move about the bulk of the electron. This is a qualitative description but there is value to it.The electron sea model proposes that all the metal atoms in a metallic solid contribute their valence electrons to form a “sea” of electrons. This sea of electron surrounds the metal cations in the lattice. 电子海模型认为所有的金属原子,在固态金属中,贡献它们的价层电子形成电子海。 By the electron-sea model, we might think that more electrons makes the bonds stronger, so hardness and melt point would increase across the periodic table. We can explain these properties using MO theory. In this case, we imagine combining many atomic orbitals (1 or more for each atom) to make and equal number of MOs that extend .Electron Sea Model. Most metal atoms do not possess enough valence electrons to enter into an ionic or covalent bonding. However, the valence electrons in metal atoms are loosely held due to their low electronegativity or attraction with the nucleus. The ionization energy of metal atoms (energy required to remove an electron from the atom) is . The electron sea model pictures the electrons on the surface of a metal being free to move from one atom to another. Due to the very low electronegativity of most metals the electrons are not held tightly by the metallic atoms.. In a covalent bond the metallic atom becomes more stable by allowing the valance electron density to be .Drude's electron sea model assumed that valence electrons were free to move in metals, quantum mechanical calculations told us why this happened. Metallic bonding in sodium. Metals tend to have high melting .
Solution. Verified by Toppr. (A) : The model of metallic bonding where electrons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms. This model proposes that all the metal atoms in a metallic solid contribute their valence electrons to form a "sea" of electron. The electrons present in the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are . To explain the observed properties of metals, a more sophisticated approach is needed than the electron-sea model commonly described. The molecular orbital theory used to explain the delocalized π bonding in polyatomic ions and molecules such as NO 2 − , ozone, and 1,3-butadiene can be adapted to accommodate the much higher number of .Electron Sea Model. Most metal atoms do not possess enough valence electrons to enter into an ionic or covalent bonding. However, the valence electrons in metal atoms are loosely held due to their low electronegativity or attraction with the nucleus. The ionization energy of metal atoms (energy required to remove an electron from the atom) is .
Properties of metals and how we can explain their properties using electron "sea" model.Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/.Correct option is A) (A) : The model of metallic bonding where electrons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms. This model proposes that all the metal atoms in a metallic solid contribute their valence electrons to form a "sea" of electron. The electrons present in the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are not held .
This means that the meter will automatically pick the correct range for things like voltage measurements. You just set the dial to DC or AC voltage, and the meter will show the correct measurements. Manual or non-auto-ranging meters require you to set the correct scale for an accurate measurement.
electron sea model|rc seaview submarine for sale